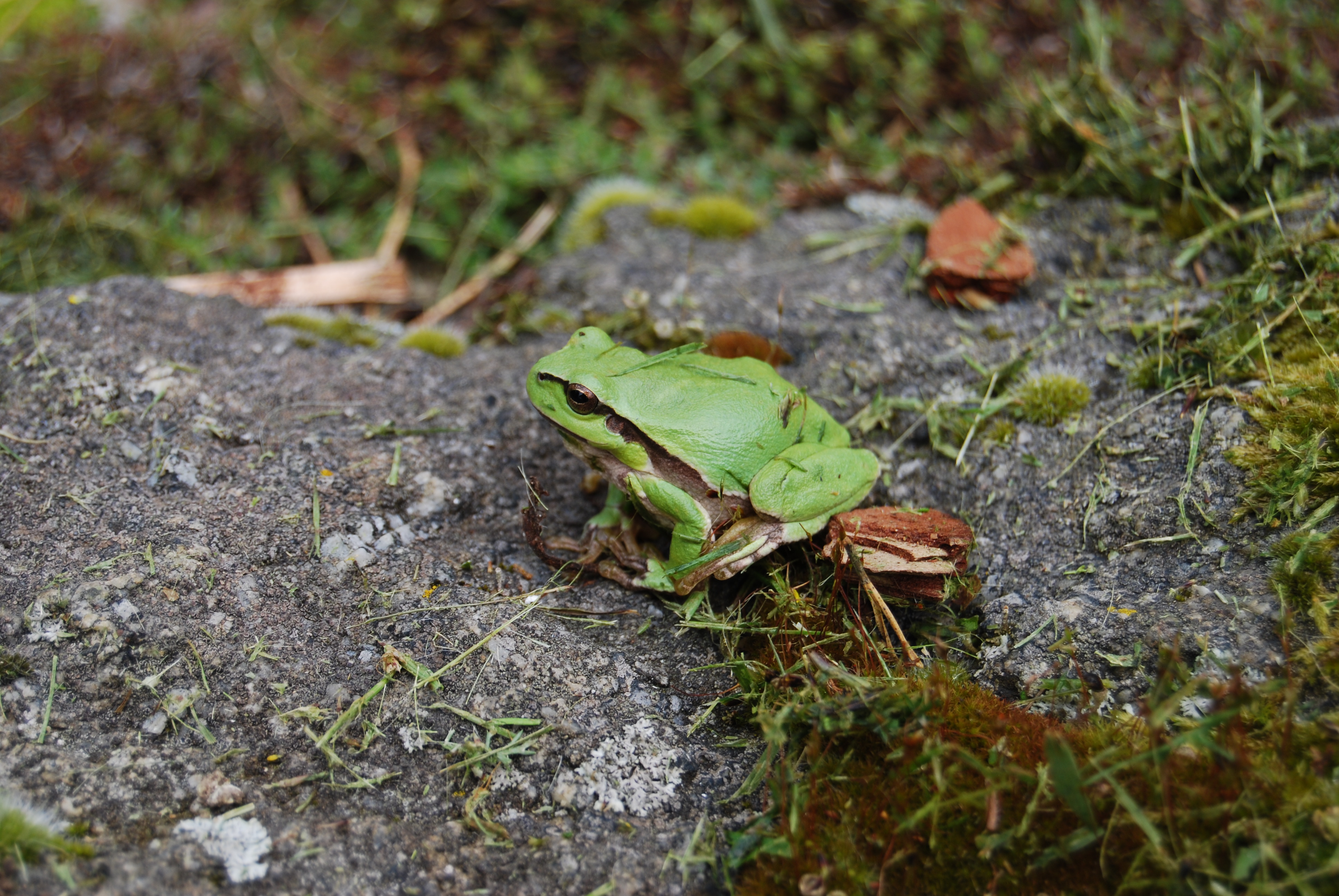
The European tree frog hides well camouflaged in the treetops thanks to the adhesive discs on its fingers and toes.
Description
The head-to-torso length of the European tree frog is 3 to 4.5 centimetres, in females up to 5 centimetres. Digits have round adhesive disks. The head is wider than it is long; the sides of the head slope steeply and the snout is correspondingly blunt-angled. The prominently protruding eyes have horizontal elliptical pupils, the sometimes dark speckled iris shines golden yellow. The surface of the skin is smooth and can be noticeably shiny, especially when sunbathing. The upper side is usually bright green in colour, but individuals can quickly change colour based on environmental characteristics. The belly and the inner surfaces of the extremities are predominantly white to light grey and granular.
Habitat
In Austria, the current populations are difficult to estimate; an important breeding site is the area around Lake Neusiedl. Depending on seasonal activity, tree frogs utilise very different aquatic and terrestrial habitats. In addition to shrubs and even treetops, various herbaceous plant species are used as perches by adults and juveniles.
Breeding call
The breeding calls of the males are announced with "aepp ... aepp ... aepp...aepp" and consist of uniform pulse groups that are clearly separated in time from each other. A series of such pulse groups forms a call. The lower call threshold is at 8 °C air temperature, the upper one at 20 to 22 °C.
Example breeding call:
Wikimedia Commons Licence Odé Baudewijn CC BY-SA 4.0 international
Source: The text is an excerpt from Wikipedia (https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Europäischer_Laubfrosch) and is available there under the licence "Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike". Status: 10 July 2023.

 DE
DE  EN
EN 









